
Reading package lists… Done -> Command executed successfully. Get:3 focal-security/main amd64 DEP-11 Metadata
#Sudo su run command update#
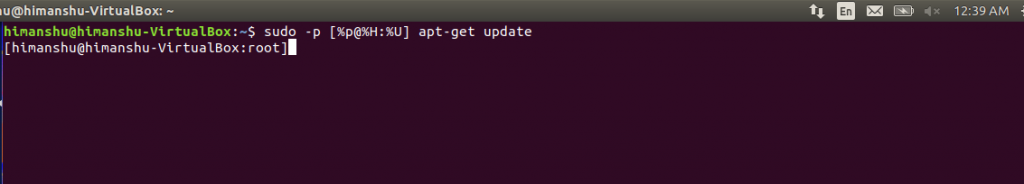
Let execute the “apt-get update” command with sudo privilege command sudo apt-get update Result- “apt-get update” needs sudo privilege to execute that’s why i encounter permission denied message. W: Problem unlinking the file /var/cache/apt/pkgcache.bin - RemoveCaches (13: Permission denied) -> Permissioned denied apt-get updateĮ: Could not open lock file /var/lib/apt/lists/lock - open (13: Permission denied) I want to update the Linux system like Ubuntu and run follwoing command without sudo privilege. ExampleĪny task which related to user ID like add user, delete user in Linux system need sudo privilege etc. In Linux system there is most of the commands need sudo privilege to execute the commands.
#Sudo su run command password#
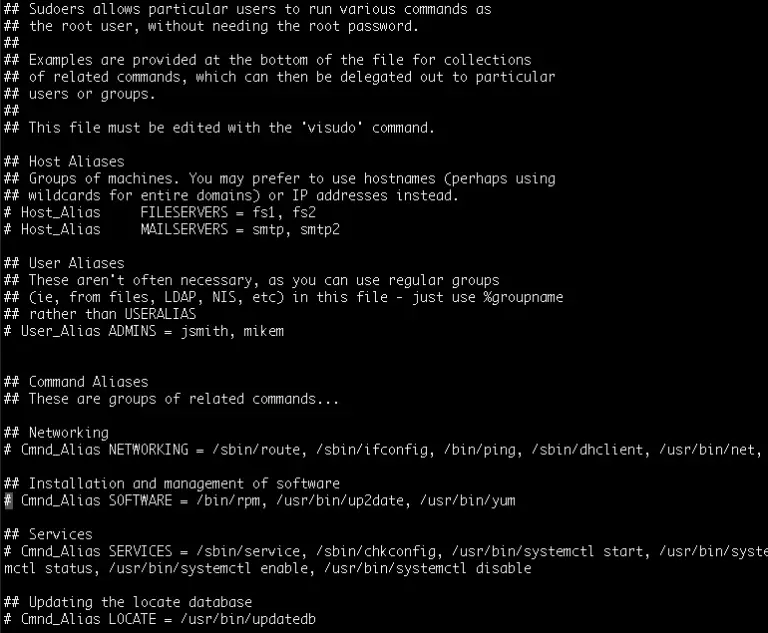
Sudo is used to run any privilege command with root privilege and asks current user logged-in password (and also checks if you’re allowed to run commands as root, which is configured through /etc/sudoers - by default all user accounts that belong to the “root” or “sudo” groups are allowed to use “sudo command”). Note: If you don’t mention username after “su -” then Linux system will assume that you want to switch to root account and will ask root password. Now run “su -” command to switch user su - /home/user2 -> User directory changed because it opens an interactive login shell

Linux “su -“privilege command opens an “ interactive login shell” that is used to switch user ( root or any standard user ) and change the current user home directory. Note: If you don’t mention username after “su” then Linux system will assume that you want to switch to root account and will ask root password. Now run su command to switch user su /home/user1 -> User directory does not change because it opens an interactive non login shell I am logged in as user1 in terminal /home/user1 Linux su privilege command opens an “ interactive non login shell” that is used to switch user ( root or any standard user ) but do not change the current user home directory.

interactive shell: A shell (login or non-login) where you can interactively type or interrupt commands.When you open a graphic terminal in gnome it is a non-login shell. non-login shell: A shell that is executed without logging in, necessary for this is a currently logged-in user.When you hit ctrl+ alt+ F1 to login into a virtual terminal you get after successful login a login shell. login shell: A login shell logs you into the system as a specified user, necessary for this is a username and password.Lets explain the difference between following Linux privilege commands:īefore going to Privilege command need to understand the type of login shell in Linux system Today i will explain which command you should use to get right privilege at right time to execute your task.
Do you know, you can get superuser privilege on your Linux system to just execute two commands but surely you don’t know about what is difference between Linux super privilege commands su, su -, Sudo su, sudo su-, sudo -s, sudo -i or sudo /bin/bash so on.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
